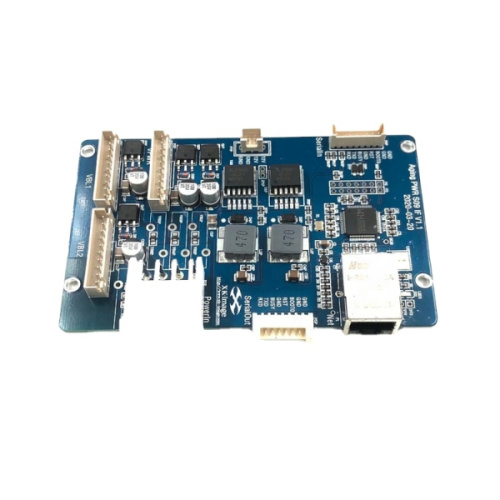
Smt And Thru-hole Custom Pcb Assembly Fr4
-
$12.00≥1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact NowWhat is SMT on PCB?
SMT is an industry abbreviation for surface mount technology. Surface mount technology for printed circuit boards or SMT PCBs is a process in which Electronic Components are placed directly on top of the circuit board instead of passing parts through the circuit board. This helps reduce manufacturing costs and increase the speed at which printed circuit board manufacturers can manufacture circuit boards. These are assembly machines that place the device on the prepared circuit board, making them an important part of the process. SMT is most cost-effective when automated, so companies usually design surface mount equipment to handle as many assembly processes as possible.

The main advantages of using SMT PCB assemblies when manufacturing printed circuit boards include:
Small size: For many products, size is one of the most important issues, and surface mount can minimize the depth required to manufacture most components. This is especially important for many modern devices (such as smartphones, tablets, and smart watches), which require the smallest possible SMT PCB boards.
Lightweight: The weight of the SMT system is only one tenth of Through-Hole Assembly. This relieves the pressure on the circuit board itself and allows companies to use less materials to cut costs and achieve low cost pcb manufacturing, which is an important reason why they use PCB SMT processes entirely
Increased flexibility: By placing some components directly on the surface, the company can leave more space for parts that cannot be placed on the surface. This provides additional flexibility in manufacturing and allows the creation of electronic products that would otherwise not be manufactured to the desired specifications.

In the PCBA Manufacturing process, although surface mount technology is very useful, you should be aware of some disadvantages.
First, the smaller lead space makes maintenance more difficult. Surface-mounted parts are usually placed very close together, perhaps even closer than the distance that many repair tools can use. This makes it very difficult to repair damaged circuit boards. If the failure rate of the parts is high, this will be a serious problem.
Second, it is difficult to ensure that the solder connection can withstand thermal cycling. Choosing an assembler that has experience with small parts is important to avoid malfunctions. Fundamentally using smaller, thinner components means that parts are more likely to fail, so if you need to minimize the failure rate and do not have the technology to mitigate risks, then SMT is not a good process.
Finally, SMT is generally not suitable for components that generate a lot of heat or have high electrical loads. This is mainly because the solder melts under the excessive heat of Wave Solder for PCBA. If the design process cannot really do the work you need, it is fundamentally bad.

Assembly techniques vary, but for safety and stability considerations, most companies manufacture printed circuit boards that are at least 18 inches by 24 inches, and then cut along a predetermined line to divide the finished board into useful components. For SMT assembly, this is much more effective than trying to print each board separately.
The surface mounting process itself starts with the pads (small dots of various metals) to which solder paste is added using an assembly machine. After adding the paste, the machine picks up the component and places it on the board.
When everything is ready, the circuit board will undergo a special heating process, which is sufficient to melt all the solder particles in the solder paste without damaging other components. With the right design, the molten paste also pulls each component into place. After that, the board is cleaned and cooled to remove all excess particles and solder paste, and then checked for defects before being shipped out.
Related Keywords