How to determine the substrate material of the PCB?
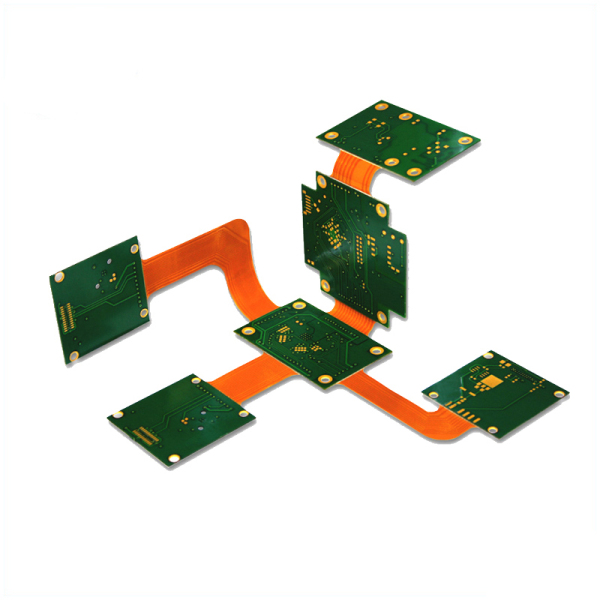
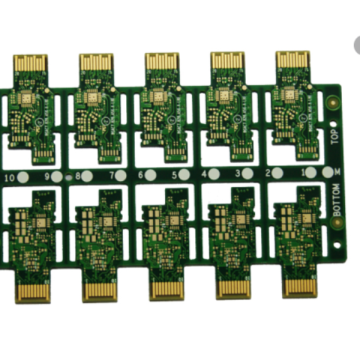
In the modern electronic age, the miniaturization and thinning of electronic equipment has necessitated the emergence of rigid PCBs and flexible/rigid PCBs. So which type of substrate material is suitable for them?
The application areas of rigid PCB and Rigid-Flex Board continue to increase, and new requirements are put forward in terms of quantity and performance. For example, polyimide films can be classified into multiple categories, including transparent, white, black, and yellow with high heat resistance and low coefficient of thermal expansion in order to be applied to different situations. Similarly, the cost-effective polyester film substrate is also accepted by the market due to its high elasticity, dimensional stability, film surface quality, photoelectric coupling and environmental resistance, to meet the changing needs of users.
Similar to rigid HDI PCB, flexible PCB must meet the requirements of high-speed and high-frequency signal transmission, and the dielectric constant and dielectric loss of flexible substrate materials must also be paid attention to. Flexible circuits can be composed of polytetrafluoroethylene and advanced polyimide substrates. Inorganic dust and carbon fiber can be added to the polyimide resin to produce a three-layer flexible thermally conductive substrate. The inorganic filler material may be aluminum nitride, aluminum oxide or hexagonal boron nitride. This type of substrate material has a thermal conductivity of 1.51W/mK, and can withstand a voltage of 2.5kV and a curvature of 180 degrees.
Flexible PCBs are mainly used in smart phones, wearable devices, medical equipment and robotics, which puts forward new requirements for flexible PCB structures. So far, some new products containing flexible PCBs have been developed, such as ultra-thin flexible multilayer PCBs whose thickness has been reduced from 0.4mm to 0.2mm. By using polyimide substrate materials with low Dk and Df, the high-speed transmission flexible PCB can reach a transmission speed of 5Gbps. High-power flexible PCBs use conductors with a thickness greater than 100μm to meet the requirements of high-power and high-current circuits. All these special flexible PCBs will naturally get unconventional substrate materials.